Privacy Preserving Image Captioning

Scene captioning, the task of describing visual information using text, typically relies on high-resolution images, raising privacy concerns due to potential exposure of sensitive data like facial attributes. This project introduces a novel solution to protect privacy by integrating optics design with algorithms, using a learned refractive lens to obscure sensitive visual attributes in the acquired image while still enabling accurate scene captions. 📸🔒
Key Features
- Privacy-Preserving Lens: A specially designed lens that distorts sensitive attributes, such as faces, ethnicity, and gender, ensuring privacy before image acquisition.
- Optimized Deep Learning: Combines an optimized refractive lens with a deep network architecture for end-to-end scene captioning from distorted images. 🤖🔍
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Validated through extensive simulations and hardware experiments, showing a superior balance between privacy and utility.
Published Papers
📌 Optics lens design for privacy-preserving scene captioning: Paula Arguello, Jhon Lopez, Carlos Hinojosa, Henry Arguello🏆BEST PAPER AWARD ICIP 2022🏆
📌 Learning to Describe Scenes via Privacy-aware Optical Lens: Paula Arguello, Jhon Lopez, Karen Sanchez, Carlos Hinojosa, Hoover Rueda-Chacón, Henry Arguello LatinX at CVPR 2024
📌 Learning to Describe Scenes via Privacy-aware Designed Optical Lens: Paula Arguello, Jhon Lopez, Karen Sanchez, Carlos Hinojosa, Fernando Rojas-Morales, Henry Arguello IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging
Results
Ablation against other privacy-preserving approaches

Robustness to deconvolution

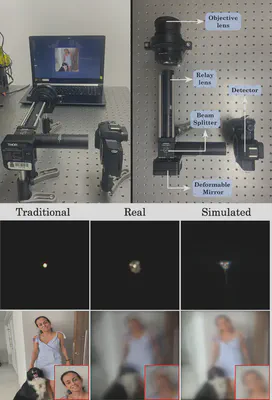
Hardware Implementation
Related Papers
Related works that you may be interested 👇
🔗 Privhar: Recognizing Human Actions From Privacy-Preserving Lens: Carlos Hinojosa, Miguel Marquez, Henry Arguello, Ehsan Adeli,Li Fei-Fei, Juan Carlos Niebles.
🔗 Learning Privacy-preserving Optics for Human Pose Estimation: Carlos Hinojosa, Juan Carlos Niebles, Henry Arguello.